Manual
Introduction
Welcome to the PDB-Tools Web manual. Here you will find information about:
- Supported input by the server
- How to save and load pipelines
- Adding, removing and moving different tools to your pipeline
- An exhaustive list of all the available pdbtools
The main entry point is the Submit page. This page offers in a single interface all the necessary actions in order to upload input and adding tool blocks to your pipeline.
Input
There are two possible ways to add data to your pipeline (Figure 1):
- Fetching structural data from Protein Data Bank.
- Uploading your data.

Fetching structural data from Protein Data Bank
If you use the Fetch interface, you need to provide a valid PDB code in the corresponding field. It is possible to download the first active biological assembly in the Protein Data Bank if you check the biounit option. In case a different biological assembly is required, it should be provided as a PDB file via the action. Once you click on the button and after waiting for a few seconds, the structure will be available (Figure 2).
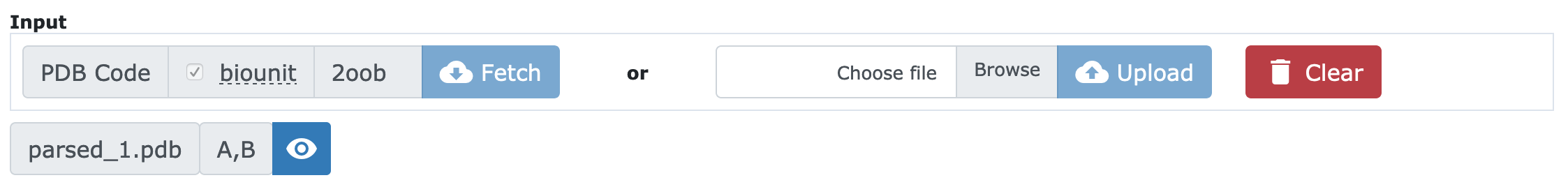
In this example, PDB structure 2OOB has been parsed and it appears with the name parsed_1.pdb. The chains found on parsing are shown (A and B) and there is a button for visualizing the structure in a 3D representation using NGL viewer.
In case you require to use a different input, you may clear using the .
Uploading your data
It is possible to upload your data in different formats. The following extensions (and formats) are supported: pdb, ent, cif, tar, tgz, bz2, tar.gz and zip.
Some of these file extensions correspond to compressed formats. In case a compressed format is detected, the service will unpack its content as different structures available as input. Take into account that the pdb-tools pipeline will be applied to each of the found structures.
Save and load pipelines
It is possible to save the current pipeline. To do it so, it is as simple as clicking on the and saving the generated JSON file to your disk. Then, it is possible to load this pipeline at any point by using the .

Customizing your pipeline with tools
Adding tools to the current pipeline is as simple as selecting the desired tool from the different block selectors and clicking on the button.

Depending on the nature of the tool, the name will be coloured in main, pre-tool or post-tool.
- pre-tool are blocks which only might be added at the beginning of the pipeline, before any other regular or merge-tool block. Only one of each type of pre-tools block is allowed at a time.
- post-tool are blocks which only might be added to the pipeline if there is already a pre-tool assigned. Its position is always to the right of any other pre-tool. Only 1 block of this is allowed.
- main blocks might be added at your convenience, in any (semantically correct) order of your choice.
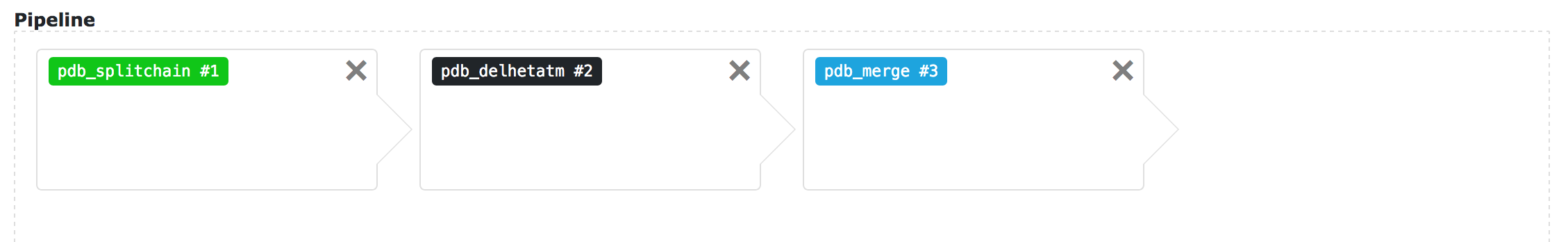
Blocks might be removed (if you click on the X) and sorted if you drag and drop them.
If you click on the button, an example pipeline with different blocks and a sample input will be loaded.
If you check the option, it will add to the end of the current pipeline the tool pdb_tidy to all generated outputs, which will modify the output to adhere (as much as possible) to the PDB format specifications.

Available PDB-Tools
Modifies the temperature factor column of a PDB file (default 10.0).
Usage
python pdb_b.py -<bfactor> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_b.py -10.0 1CTF.pdb
Modifies the chain identifier column of a PDB file (default is an empty chain).
Usage
python pdb_chain.py -<chain id> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_chain.py -C 1CTF.pdb
Renames chain identifiers sequentially, based on TER records
Usage
python pdb_chainbows.py <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_chainbows.py 1CTF.pdb
Replaces the segment identifier column by the value in the chain identifier column of the PDB file.
Usage
python pdb_chainxseg.py <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_chainxseg.py 1CTF.pdb
Performs a basic check on a multi-model PDB file (ensemble) to ensure all models are have exactly the same atoms (as they should).
Usage
python pdb_chkensemble.py <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_chkensemble.py 1CTF.pdb
Deletes all atoms matching specific chains in the PDB file.
Usage
python pdb_delchain.py -<option> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_delchain.py -A 1CTF.pdb # removes chain A from PDB file
Deletes all atoms matching the given element in the PDB file. Elements are read from the element column.
Usage
python pdb_delelem.py -<option> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_delelem.py -H,N 1CTF.pdb # deletes all protons and nitrogens
Removes all HETATM records in the PDB file.
Usage
python pdb_delhetatm.py <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_delhetatm.py 1CTF.pdb
Deletes a range of residues from a PDB file. The range option has three components: start, end, and step. Start and end are optional and if ommitted the range will start at the first residue or end at the last, respectively. The step option can only be used if both start and end are provided. Note that the start and end values of the range are purely numerical, while the range actually refers to every N-th residue, regardless of their sequence number.
Usage
python pdb_delres.py -[resid]:[resid]:[step] <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_delres.py -1:10 1CTF.pdb # Deletes residues 1 to 10
Removes all residues matching the given name in the PDB file. Residues names are matched *without* taking into consideration spaces.
Usage
python pdb_delresname.py -<option> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_delresname.py -ALA 1CTF.pdb # removes only Alanines
Assigns the element column to the PDB file, guessing the element from the atom
Usage
python pdb_element.py <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_element.py 1CTF.pdb
Fixes insertion codes in a PDB file.
Usage
python pdb_fixinsert.py [-<option>] <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_fixinsert.py -A9,B12 1CTF.pdb # deletes ins. codes for residue 9 of chain A and 12 of chain B.
Detects gaps between consecutive residues in the sequence, both by a distance criterion or discontinuous residue numbering. Only applies for protein residues.
Usage
python pdb_gap.py <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_gap.py 1CTF.pdb
Returns the first N coordinate (ATOM/HETATM) lines of the file.
Usage
python pdb_head.py -<num> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_head.py -100 1CTF.pdb # first 100 ATOM/HETATM lines of the file
Removes all non-coordinate records from the file. Keeps only MODEL, ENDMDL, END, ATOM, HETATM, and CONECT.
Usage
python pdb_keepcoord.py <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_keepcoord.py 1CTF.pdb
Modifies the occupancy column of a PDB file (default 1.0).
Usage
python pdb_occ.py -<occupancy> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_occ.py -1.0 1CTF.pdb
Renumbers atom serial numbers of the PDB file starting from a given value (default 1).
Usage
python pdb_reatom.py -<number> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_reatom.py -10 1CTF.pdb # renumbers from 10
Renumbers the residues of the PDB file starting from a given number (default 1).
Usage
python pdb_reres.py -<number> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_reres.py -10 1CTF.pdb # renumbers from 10
Performs in-place replacement of a chain identifier by another.
Usage
python pdb_rplchain.py -<from>:<to> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_rplchain.py -A:B 1CTF.pdb # Replaces chain A for chain B
Performs in-place replacement of a residue name by another. Affects all residues with that name.
Usage
python pdb_rplresname.py -<from>:<to> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_rplresname.py -HIP:HIS 1CTF.pdb # changes all HIP residues to HIS
Modifies the segment identifier column of a PDB file (default is an empty segment).
Usage
python pdb_seg.py -<segment id> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_seg.py -C 1CTF.pdb
Replaces the chain identifier column by the value in the segment identifier column of the PDB file. Truncates the segment identifier if longer than one character.
Usage
python pdb_segxchain.py <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_segxchain.py 1CTF.pdb
Selects one location for each atom with fractional occupancy values. By default, selects the label with the highest occupancy value for each atom, but the user can define a specific altloc label to select.
Usage
python pdb_selaltloc.py [-<option>] <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_selaltloc.py 1CTF.pdb # picks locations with highest occupancy
Selects all atoms matching the given name in the PDB file. Atom names are matched without taking into consideration spaces, so ' CA ' (alpha carbon) and 'CA ' (calcium) will both be kept if -CA is passed.
Usage
python pdb_selatom.py -<option> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_selatom.py -CA 1CTF.pdb # keeps only alpha-carbon atoms
Extracts one or more chains from a PDB file.
Usage
python pdb_selchain.py -<chain id> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_selchain.py -C 1CTF.pdb # selects chain C
Selects all atoms that match the given element(s) in the PDB file. Elements are read from the element column.
Usage
python pdb_selelem.py -<option> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_selelem.py -H 1CTF.pdb # selects all protons
Selects all HETATM records in the PDB file.
Usage
python pdb_selhetatm.py <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_selhetatm.py 1CTF.pdb
Extracts residues from a PDB file, either arbitrarily or in a range. The range option has three components: start, end, and step. Start and end are optional and if ommitted the range will start at the first residue or end at the last, respectively.
Usage
python pdb_selres.py -[resid]:[resid]:[step] <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_selres.py -1,2,4,6 1CTF.pdb # Extracts residues 1, 2, 4 and 6
Selects all residues matching the given name in the PDB file. Residues names are matched *without* taking into consideration spaces.
Usage
python pdb_selresname.py -<option> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_selresname.py -ALA 1CTF.pdb # keeps only Alanines
Extracts one or more segments from a PDB file based on their segment identifiers.
Usage
python pdb_selseg.py -<segment id> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_selseg.py -C,D 1CTF.pdb # selects segment C
Renumbers the residues of the PDB file by adding/subtracting a given number from the original numbering.
Usage
python pdb_shiftres.py -<number> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_shiftres.py -10 1CTF.pdb # adds 10 to the original numbering
Sorts the ATOM/HETATM/ANISOU/CONECT records in a PDB file.
Usage
python pdb_sort.py -<option> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_sort.py 1CTF.pdb # sorts by chain and residues
Converts a PDB file to the mmCIF format. Will convert only the coordinate
Usage
python pdb_tocif.py <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_tocif.py 1CTF.pdb
Extracts the residue sequence in a PDB file to FASTA format. Canonical amino acids and nucleotides are represented by their one-letter code while all others are represented by 'X'. The -multi option splits the different chains into different records in the FASTA file.
Usage
python pdb_tofasta.py [-multi] <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_tofasta.py 1CTF.pdb
Renames atoms sequentially (C1, C2, O1, ...) for each HETATM residue. Relies on an element column being present (see pdb_element).
Usage
python pdb_pdb_uniqname.py <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_pdb_uniqname.py 1CTF.pdb
Validates the PDB file ATOM/HETATM lines according to the format specifications.
Usage
python pdb_validate.py <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_validate.py 1CTF.pdb
Summarizes the contents of a PDB file, like the wc command in UNIX.
Usage
python pdb_wc.py <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_wc.py 1CTF.pdb
Splits a PDB file into several, each containing one chain.
Usage
python pdb_splitchain.py <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_splitchain.py 1CTF.pdb
Splits a PDB file into several, each containing one MODEL.
Usage
python pdb_splitmodel.py <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_splitmodel.py 1CTF.pdb
Splits a PDB file into several, each containing one segment.
Usage
python pdb_splitseg.py <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_splitseg.py 1CTF.pdb
Merges several PDB files into one. The contents are not sorted and no lines are deleted (e.g. END, TER statements) so we recommend to enable the Tidy option
Usage
python pdb_merge.py <pdb file> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_merge.py 1ABC.pdb 1XYZ.pdb
Merges several PDB files into one multi-model (ensemble) file. Strips all HEADER information and adds REMARK statements with the provenance of each conformer.
Usage
python pdb_mkensemble.py <pdb file> <pdb file>
Example
python pdb_mkensemble.py 1ABC.pdb 1XYZ.pdb





